HOW IT WORKS
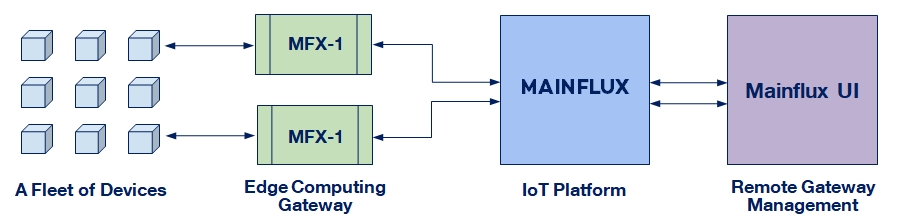
Mainflux IoT Edge Gateways works within system which consists following components:
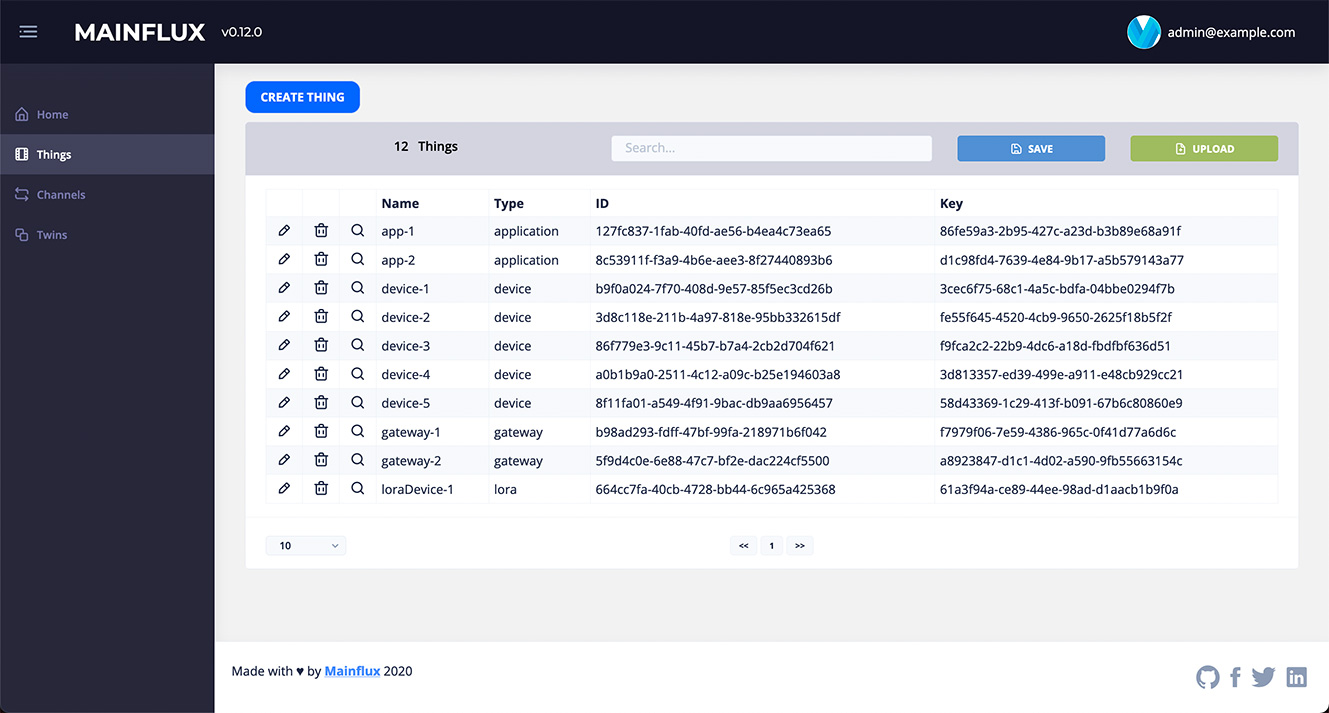
1) Devices - Sensors and actuators
2) IoT Edge Computing Gateway - MFX-1 with based on Mainflux IoT Platform
3) Mainflux IoT Core Platform - Open-source patent – free IoT Platform
4) Mainflux UI - A system for remote device and gateways management
Mainflux IoT Core Platform and UI – Remote Gateway Management
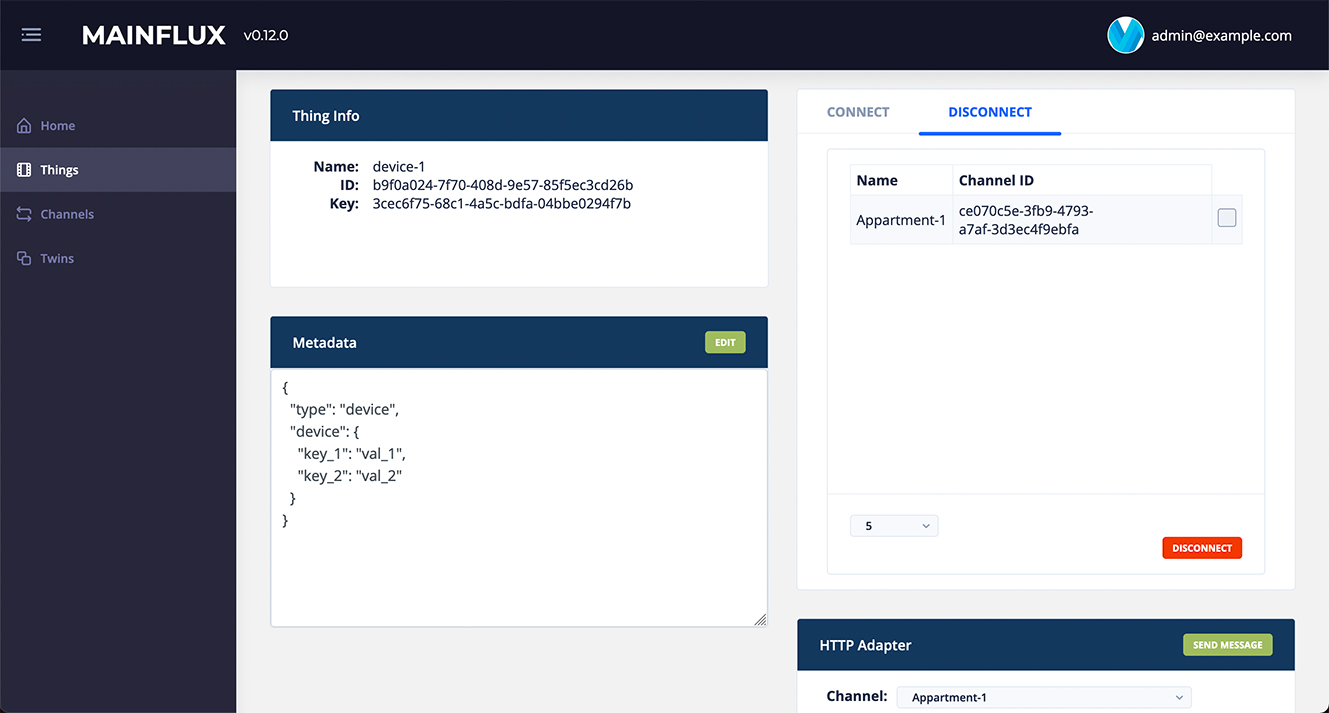
Mainflux IoT Core Platform accepts connections from the gateways on the south side. Each gateway has dedicated channels (at least).
On the north side, Mainflux is connected to UI, and serves as a middleware (messaging bridge) between gateway management and data acquisition apps in the cloud and thousands of remote gateways in the field.
Mainflux has several important roles:
• Control plane communication - commands for gateway management
• Data plane communication - data acquisition and storage
• Bootstrapping - initial gateway config, plug-and-play for factory devices
Mainflux UI gives visualisation and monitoring of the gateways:
• Metrics from each of the gateway (CPU, memory, networking)
• Map geopositioning
• Various logs
One of the most important features of remote gateway management are Secure Remote Terminal and Secure Remote Browser.
Secure Remote Terminal
Secure Remote Terminal is basically Linux terminal - to - MQTT(S) proxy, that lets apps in the cloud open remote and secure SSH-like sessions,
but without a need for heavy VPN infrastructure to be maintained (these infrastructures in the cloud present heavy burden for operators,
as they are complex and expensive. Moreover, gateways act as SSH servers and need to keep ports open to accept connections).
Gateway MQTT connections are client initiated (no need to open extra ports on gateway), secured with PKI X.509 certificates and encrypted via mTLS.
This innovation allows very lightweight, simple and secure logging into each of remote gateways, executing commands interactively, opening and editing files, debugging and so on.
This innovation allows very lightweight, simple and secure logging into each of remote gateways, executing commands interactively, opening and editing files, debugging and so on.
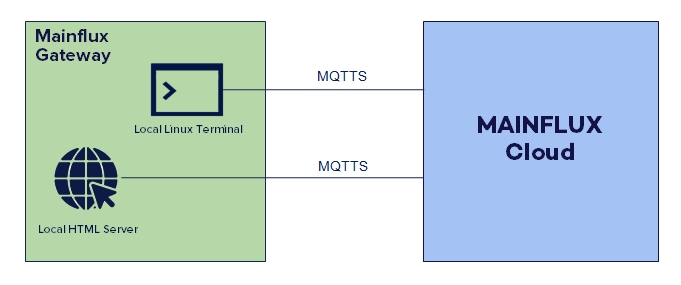
Secure Remote Browser
Similar to Secure Remote Terminal, Secure Remote Browser is HTTP-to-MQTT proxy, that bundles HTTP requests and responses into MQTT messages.
These HTTP req/resp are executed on a gateway itself, as often on the gateway there is a local web browser that serves configuration or other web pages.
Typically these web servers on gateways are accessed via VPN, which again means that gateway needs to keep port 80 open as well.
Mainflux Edge avoids heavy VPN infrastructure, and uses lightweight technology to wrap HTML content into secure MQTT messages and send them
to the cloud, where this content is examined in the browser and acts like the browser actually accessed the server on the gateway itself.
Again - benefits are simplified infrastructure and higher security, as MQTT connections are client-initiated, so gateways can close port 80
(and all other ports) for external access.
Mainflux IoT Agent - Linux Daemon Agent – Gateway Remote Management Enabler
Mainflux IoT Agent is a Linux daemon agent that runs on the remote gateway and connects to Mainflux cloud in order to enable remote management,
monitoring and alerting and the Control Plane of the gateway. It is subscribed via MQTT to Mainflux IoT Core Platform on the CMD channel.
It gets commands from Mainflux, executes them on the gateway and returns responses to Mainflux.
It configures and manages all other services on the gateway, as well as aforementioned remote terminal and remote browser.
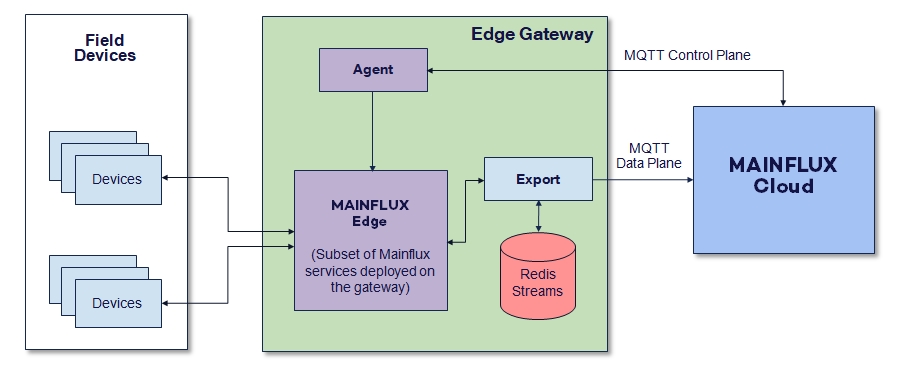
Export Service – Gateway Data Acquisition With Buffering
Export service is used to send data from gateway to Mainflux cloud. One of the common problems with IoT gateways are intermittent connections due poor network reliability (especially with moving objects). Export service is an intelligent service: it constantly monitors the network availability and in the case of disconnection it buffers data locally, so none of the data points are lost. When the network comes back on, Export service sends a buffered data stream
to the cloud while preserving order of messages.